Written by Simran Ahluwalia | Artist by Simran Ahluwalia
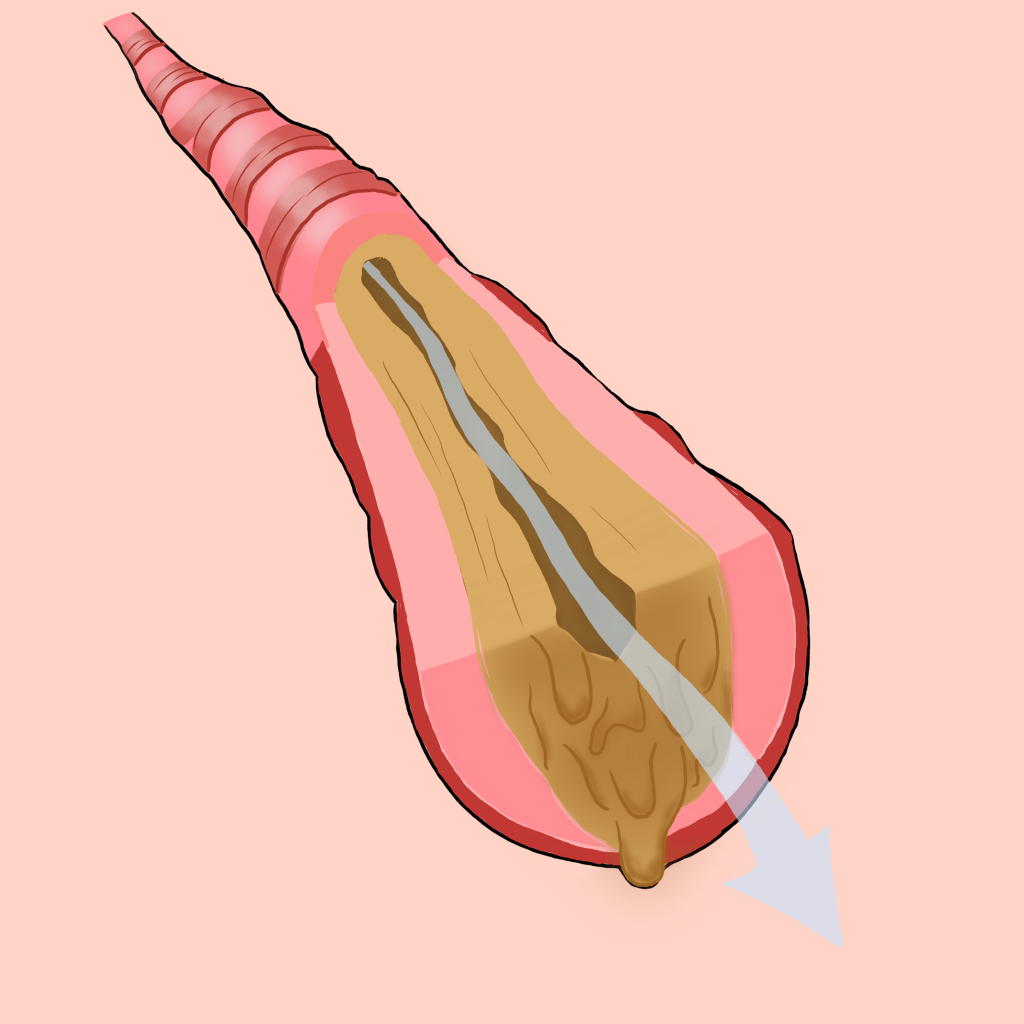
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic condition that affects proteins in the body. People with this condition have a faulty gene that affects their cells, tissue, and the glands that make mucus and sweat. Many people carry the cystic fibrosis gene but do not carry symptoms as a person with CF must inherit two defective recessive genes, one from each parent. Mucus in people with cystic fibrosis is extremely thick and sticky while normal mucus is usually slippery,protecting the airways, digestive tracts, and other organs and tissues. This can cause severe damage to the lungs, digestive system, and other organs. It is one of the most chronic lung diseases in children and young adults, making it extremely important to educate ourselves and spread awareness about this disease!
Because of newborn screening, cystic fibrosis can be diagnosed within the first month of life, before the symptoms develop. Symptoms may worsen or improve as time goes on, and some people may not experience symptoms until their teenage or adult years. Symptoms can vary person to person but there are common ones. People with cystic fibrosis often can have a recurring inflamed pancreas (pancreatitis), infertility, recurring pneumonia, and higher levels of salt concentration in their sweat. The thick mucus and clog the tube that carries air in and out of the lungs, causing certain nasal and respiratory symptoms. These include persistent coughing that produces thick mucus (sputum), wheezing, exercise intolerance, repeated lung infections, inflamed nasal passages or stuffy noses, or recurring sinusitis. Additionally, the thick mucus can also block the tubes that carry digestive enzymes from your pancreas to your small intestine, causing certain digestive symptoms. These include smelling and greasy stool, poor weight gain and growth, intestinal blockage (especially in newborns), and chronic or severe constipation, which can lead to rectal prolapse.
Medical professionals have certain methods to diagnose cystic fibrosis. In newborn screenings, few drops of blood are taken while the newborn is still in the hospital and places the drops of blood on a Guthrie card. This screening looks for a list of conditions which includes CF. Every U.S state requires this test. In a sweat test, the amount of chloride in the body’s sweat is measured, as those with CF have a high concentration of chloride. In the tests, a chemical called pilocarpine is spread on the skin. Afterwards, a small amount of electrical stimulation is applied to encourage the sweat glands to produce sweat, which is collected in a plastic coil or on a piece of filter paper or gauze. This is the most conclusive test for CF. In genetic tests, blood samples are tested for the genes that cause CF. Chest and sinus x-rays are used to support or confirm CF, but other tests need to be done with this as well. In lung function tests, a spirometer is used. One must breathe in completely and then push the inhaled breath into the mouthpiece of the spirometer. With sputum culture tests, doctors will take a sample of sputum and test it for bacteria like Pseudomonas as they are most commonly found in people with cystic fibrosis. In nasal potential difference tests (NPD), a voltmeter and electrode are placed into and out of the nose to measure the electricity generated by the transfer of ions in the solution across nasal tissue.
Cystic fibrosis is a chronic condition and there is no cure for it, but there are ways to manage the symptoms. The main focus is to keep the airways clear which can be done in a number of ways. Special ways of breathing and coughing can be learned, and devices that fit into the mouth or therapy vests can use vibrations to loosen the mucus. Chest physical therapy, also known as postural drainage and percussion can be learned to loosen to mucus as well. With this method, the lungs can be moved into certain positions to allow them to drain properly. Additionally medicines can be used to aid CF symptoms. Antibiotics can be used to treat lung infections that come with CF. Inhaled bronchodilators can make breathing easier by opening and relaxing the airways. Inhaled medicine can make mucus thinner and easier to get rid of. Additionally, anti-inflammatory drugs, pancreatic enzymes to aid in digestion and stool softener to help with digestion can also be used. Lastly, surgeries on the nose, sinuses, bowels can be done, and transplant surgeries on the lungs or liver can be implemented as well.
In conclusion, cystic fibrosis remains a challenging condition with a large impact on patients’ lives. While advancements in treatments have improved outcomes, there is still much to be done to enhance the quality of life and life expectancy for those affected by this genetic disorder. Continued support for research, early detection, and innovative therapies are crucial in the ongoing fight against cystic fibrosis.
Works Cited:
“Cystic Fibrosis (CF).” Pennmedicine.Org, http://www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/cystic-fibrosis. Accessed 30 Apr. 2024.
“Cystic Fibrosis.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 23 Nov. 2021, http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cystic-fibrosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20353700.
professional, Cleveland Clinic medical. “Cystic Fibrosis (CF): Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment.” Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9358-cystic-fibrosis. Accessed 30 Apr. 2024.
“What Is Cystic Fibrosis?” National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/cystic-fibrosis#:~:text=Cystic%20fibrosis%20(CF)%20is%20a,and%20other%20organs%20and%20tissues. Accessed 30 Apr. 2024.

Leave a comment