Written by Akemi Li | Art by Nourah Bakary
Pneumonia is a lung infection that causes air sacs to fill with fluid or pus, typically caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Symptoms may include cough, fever, chills, and headaches, with severity varying based on age, health conditions, and infection type.
This infection could be life-threatening for infants, young children, and elderly people aged 65 or older. It is also a serious problem for those who have weak immune systems and are diagnosed with other health problems such as asthma, heart disease, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Pneumonia’s complications include bacteremia, an infection that can spread to other organs through the bloodstream. Pneumonia can also cause fluid build-up, which can accumulate around the lungs, potentially requiring drainage. It is essential to look out forung abscesses as they can cause pus-filled cavities in the lungs. If an individual has this complication, they can treat it with antibiotics or surgical intervention. Another common complication is breathing difficulties, in which severe cases may require hospitalization and ventilator support.
With a visit to the clinic, a typical doctor’s procedure of diagnosis involves a medical history review, a physical exam using a stethoscope to listen for abnormal lung sounds, and tests like chest X-rays. Other possible tests may include blood tests to confirm infection and potentially identify the cause of the infection, pulse oximetry to measure blood oxygen levels, and sputum tests to analyze lung fluid and determine infection type. Treatments depend on the cause and may include medications. Mild cases can be simply treated at home, but severe pneumonia might require hospitalization for IV antibiotics and oxygen therapy.
Prevention for this disease is possible through vaccines for pneumonia and flu, good hygiene, especially hand washing, and maintaining overall health such as avoiding smoking and proper sleep, exercise, and nutrition. It is also highly recommended that infants receive the appropriate vaccinations. Recovery can take several weeks, and patients should consult healthcare providers if symptoms worsen.
Works Cited:
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. “Pneumonia” National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, 2022, https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/pneumonia/symptoms
Mayo Clinic. “Pneumonia” Mayo Clinic, 2020, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pneumonia/symptoms-causes/syc-20354204#:~:text=Pneumonia%20is%20an%20infection%20that,and%20fungi%2C%20can%20cause%20pneumonia.
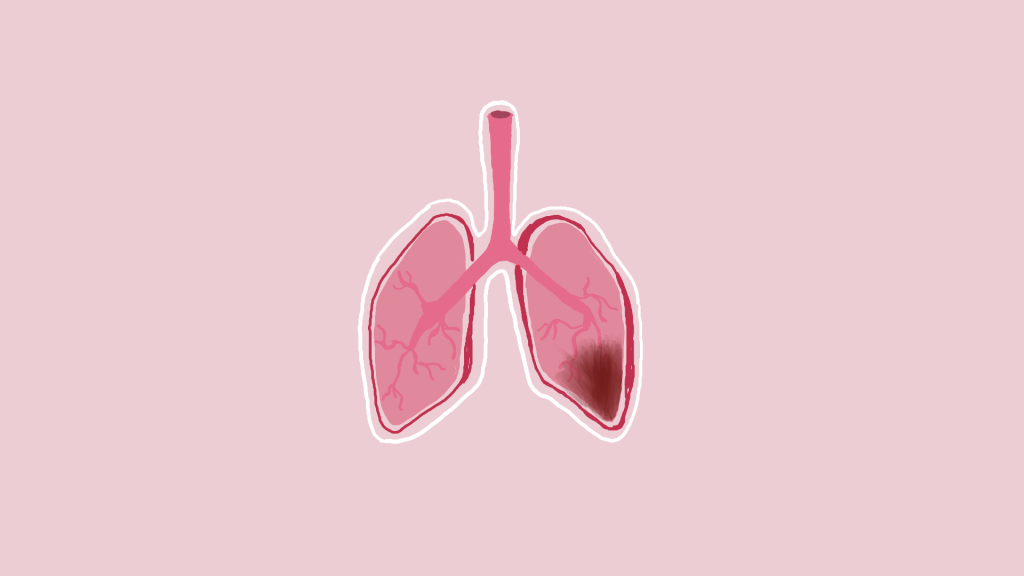

Leave a comment