Written by Srivalli Adarapu | Art by Lily Ozaeta
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, are becoming increasingly prevalent with each passing day. The Alzheimer’s Disease International predicts that by 2050, there will be around 135 million global cases of Alzheimer’s. As neurodegenerative disease cases continue to amplify, it is imperative to understand these diseases better! Neurodegenerative disorders generate a wide spectrum of symptoms affecting the entire body as a result of the gradual damage of neurons. While medications and treatments help in moderating neurodegenerative disorders, they are limited to addressing symptoms rather than offering a cure. This lack of a definitive cure stems from a limited understanding of neurodegenerative disorders, emphasizing the urgent need for further research. This article will cover five of the most common neurodegenerative diseases: Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, ALS, and Prion disease, and their impacts.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most prevalent neurodegenerative disease. This disorder progressively weakens one’s memory and cognitive abilities, eventually leading to difficulties in daily tasks. An accumulation of proteins such as amyloid and tau around brain cells, or neurons, disturbs the brain function and consequently results in this disorder. Alzheimer’s generally results in behavior and mood changes, difficulty in talking and swallowing, and confusion as the brain progressively weakens. Those who are 65 and older have the greatest risk of developing Alzheimer’s. Unfortunately, Alzheimer’s has no cure yet. However, treatments such as aducanumab and lecanemab can reduce the impacts of Alzheimer’s by eradicating amyloid proteins that build up around neurons.
Parkinson’s, the second most common neurodegenerative disease, results from the destruction of dopamine-producing neurons. These neurons are responsible for regulating behavioral processes and movement. Beyond weakening the physical body, this disease also impairs the brain. Symptoms include tremors, balancing issues, slow thinking, depression, and memory loss. While there are no cures, a variety of treatments can slow the progression of Parkinson’s.
Huntington’s disease is a hereditary condition in which regions of the brain responsible for controlling voluntary movement are impaired. Symptoms include abnormal body movement and posture, weakened memory and thinking skills, and behavioral problems. This disorder is triggered by a gene mutation for a protein called huntingtin. Treatments and medications can help minimize complications caused by Huntington’s.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, or ALS, is a neurodegenerative disease that affects one’s motor skills. Nerve cells break down, impairing motion and weakening muscles. Symptoms range but worsen over time. Some symptoms include muscle twitches and difficulty chewing, swallowing, and breathing. ALS has no defined cause but can be inherited through a gene mutation.
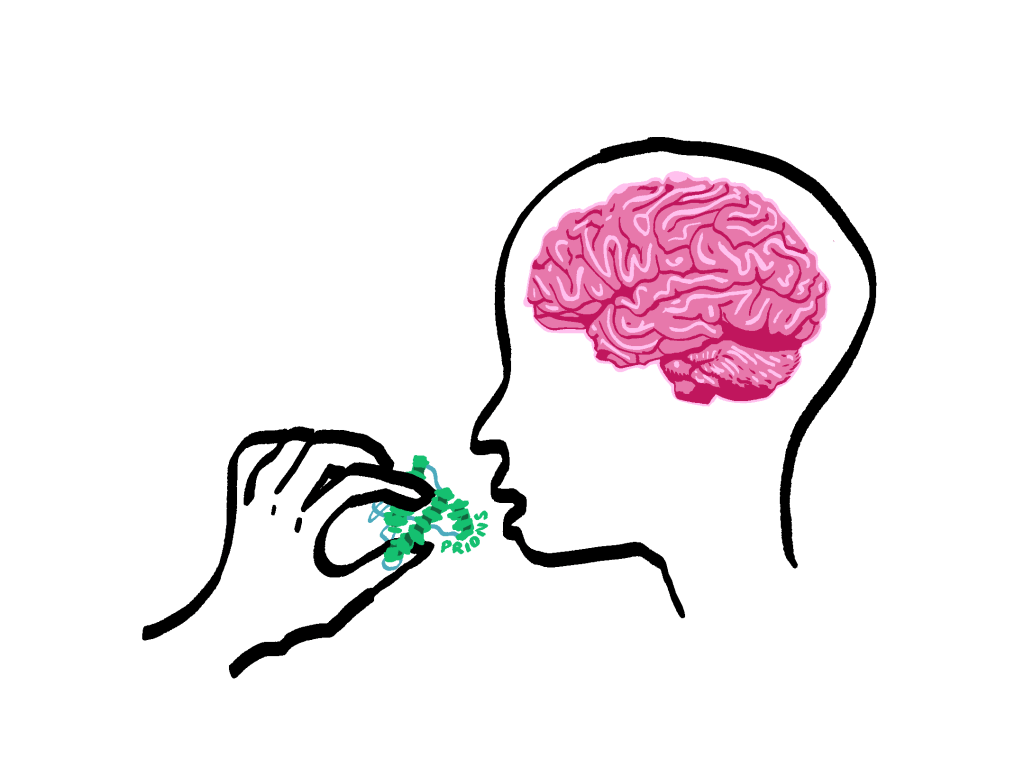
Prion diseases refer to a group of neurodegenerative disorders caused by “prions.” Unlike other disorders listed above, this disease is much rarer. According to John Hopkins Medicine, 300 cases are diagnosed annually in the United States. Prions are transmissible agents that cause proteins in the brain to become misfolded. These abnormally folded proteins result in brain damage. Prion diseases affect both animals and humans and induce a variety of symptoms depending on the disease.
Fortunately, many ongoing research projects actively focus on addressing neurodegenerative diseases and exploring possible treatments. Although these diseases can evoke much fear and trepidation, we have the opportunity to confront them by fostering greater public awareness and a comprehensive understanding of neurodegenerative diseases.
Works Cited:
“What Is Alzheimer’s?” Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia, 2024, https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers.
Parkinson’s Foundation. “What Is Parkinson’s?” Parkinson’s Foundation, 2024, https://www.parkinson.org/understanding-parkinsons/what-is-parkinsons.
Mayo Clinic. “Huntington’s Disease.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 17 May 2022, http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/huntingtons-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20356117#:~:text=Huntington’s%20disease%20is%20a%20rare,(cognitive)%20and%20 psychiatric%20 disorders.
ALS Association. “What Is Als?” The ALS Association, 2024, http://www.als.org/understanding-als/what-is-als.
John Hopkins Medicine. “Prion Diseases.” Johns Hopkins Medicine, 8 Aug. 2021, http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/prion-diseases.

Leave a comment